Welcome to your comprehensive guide to battery swapping station in Bangladesh—the fast‑track solution transforming EV energy replenishment across Dhaka, Chittagong, and beyond. As Bangladesh accelerates its shift toward clean mobility, smart swap stations emerge as critical infrastructure, offering rapid battery exchanges, real‑time IoT monitoring, and cloud‑based fleet management. Explore how battery swapping station in Bangladesh deployments minimize downtime for rickshaws, motorcycles, and light EVs, while delivering safe, reliable service backed by international certifications and local manufacturing partnerships.

Since 2022, Bangladesh’s government has introduced EV subsidies and green‑fuel mandates to curb urban pollution. Under the “Surokkha Paribahan” initiative, pilot swap‑station projects have launched in Dhaka’s cantonment and Mirpur, focusing initially on auto‑rickshaws and delivery fleets. The popularity of electric three‑wheelers—over 15,000 registered by mid‑2024—has driven investment from local startups and global players like SRE Power.
Policy Support: The Bangladesh Road Transport Authority plans to mandate swap‑station access plans for new EV permits in 2025, while fiscal incentives offset up to 30% of capital costs.
Looking ahead, spurred by the target of 500,000 EVs by 2030 and escalating urban congestion, battery swapping station in Bangladesh networks are poised for rapid expansion—evolving from small‑scale pilots to city‑wide intelligent grids.
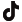



SRE Power, a Leading Innovator of EV Charging and Swap Station Solutions & Manufacturers since 2014, combines Shenzhen R&D with factories in Dongguan, Malaysia, and Africa. Certifications include CE, ISO 9001 quality management, IP65, and OCPP compliance—ensuring SRE stations meet international safety and performance standards. These attributes make SRE Swap Stations ideal for battery swapping station in Bangladesh projects demanding uptime, scalability, and local service support.
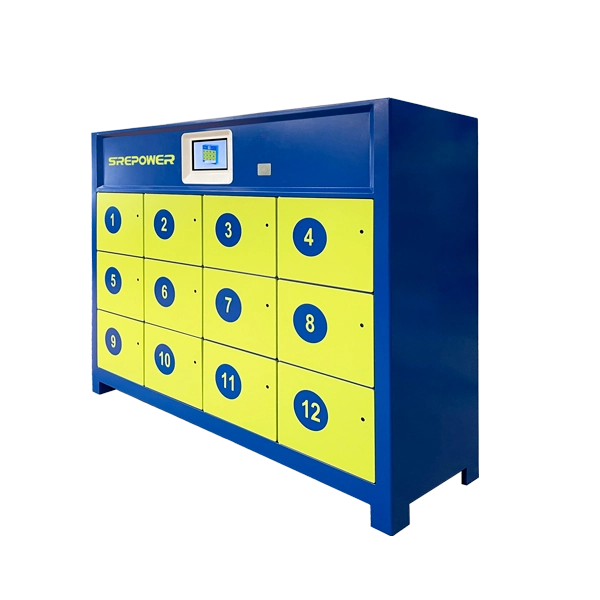

Fast – Flexible – Cloud‑Managed Battery Exchange for electric motorcycle, scooter, tricycle
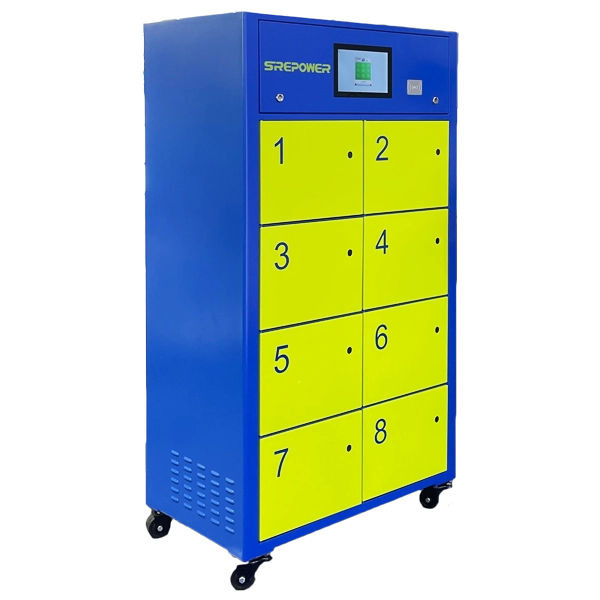

One-stop solution for convenient battery Exchange
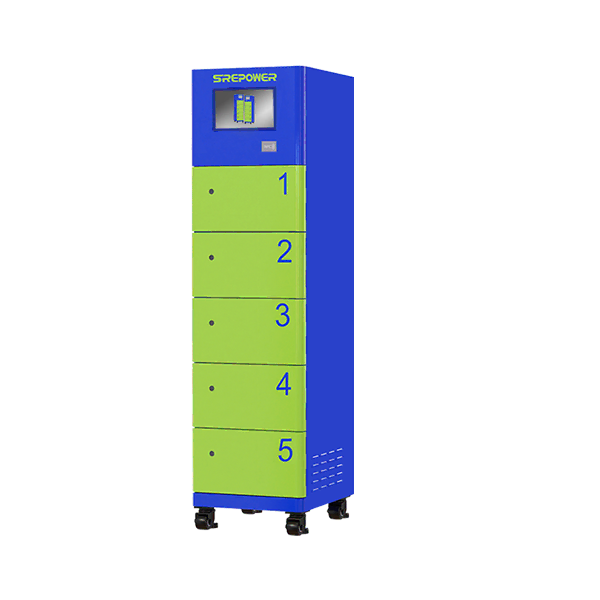

Rapid, Modular 5‑Slot Battery Exchange with Intelligent Cloud Management for Fleet Efficiency
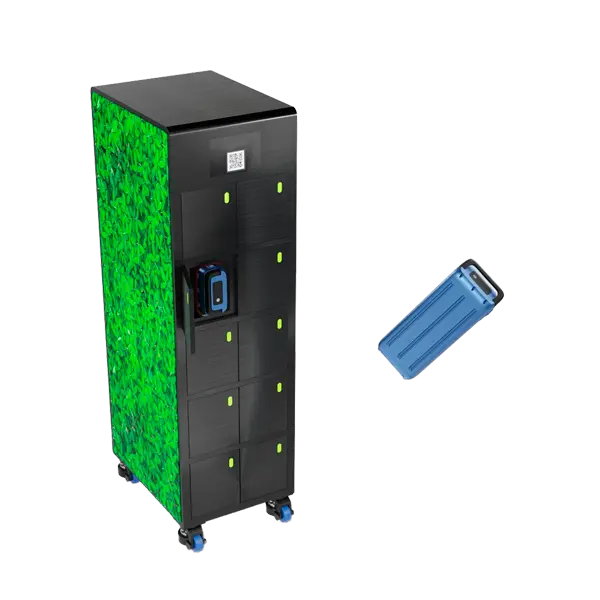

The Best Battery Swap Cabinet Solution Supplier in China
Auto‑Rickshaw Fleets:
Dhaka’s iconic CNG auto‑rickshaws convert to electric, swapping packs mid‑shift to maintain continuous service.
Last‑Mile Logistics:
E‑cargo trikes and delivery scooters exchange batteries at micro‑hubs in industrial zones—minimizing downtime during peak hours.
Ride‑Hailing Motorcycles:
Pathao and Shohoz riders use app‑linked swap stations near major junctions to extend operating hours.
Residential and Commercial Zones:
Community swap cabinets in apartment complexes and malls serve private EV owners for emergency top‑ups.
Corporate and Institutional Fleets:
University campuses and corporate parks deploy swap stations for staff electric golf carts and service vehicles.
SRE Power’s lineup—from 5‑Cabinet 15.8 kW to 12‑Cabinet 15.8 kW Smart Swap Stations—delivers:
Flexible Scalability: Start with 4 slots; expand to 24 as demand grows.
High‑Power Output: Up to 16.8 kW per slot supports rapid recharging of high‑capacity packs.
Cloud‑Native Platform: Real‑time fleet dashboards, user apps, and remote diagnostics via MQTT/OCPP.
User‑Centric UX: Multi‑modal authentication (NFC, QR, app), visual LED indicators, and guided swap flow.
Cost Efficiency: In‑house production and CKD/SKD options reduce CapEx and expedite local assembly.
These advantages position SRE solutions at the forefront of the battery swapping station in Bangladesh rollout.
An automated cabinet network where EV drivers exchange depleted packs for fully charged ones in seconds.
Typically BDT 20–BDT 50 per swap (≈$0.20–$0.50), varying by battery size and operator.
As of mid‑2025, over 30 public swap hubs in Dhaka and Chittagong.
Identification plus mechanical exchange takes 10–20 seconds.
Yes—ISO/CE‑certified packs tracked via IoT for SoC/SoH.
Stations are concentrated at transport hubs, major Search the operator’s app for nearest hubs in your area.
Electric scooters, motorcycles, auto‑rickshaws, and light EVs (36V–72V).
Centralized BMS balances cycles to maximize lifespan.
Real Estate Scarcity & Costs
Dhaka’s land shortages and high rental rates (BDT 500–2,000/sq ft) complicate site acquisition for 10–30 m² swap hubs.
Zoning approvals can take 3–6 months, delaying deployment timelines.
Standardization & Interoperability
Diverse battery formats (36 V–72 V, 27–100 Ah) across local EV models require modular cabinets and extensive compatibility testing.
Absence of unified national battery‑pack standards increases inventory complexity and spare‑parts overhead.
Grid Stability & Energy Costs
Frequent load‑shedding, voltage fluctuations, and high industrial tariffs (BDT 8–12/kWh) necessitate BESS buffering and on‑site solar—raising CapEx.
Peak demand charges and surcharges further increase OpEx for high‑throughput stations.
Consumer Awareness & Trust
Limited public familiarity with swapping models breeds skepticism around battery quality and safety.
Education campaigns and visible ISO/CE certifications are needed to build confidence among rickshaw‑drivers and fleet operators.
Upfront Investment vs. ROI
High initial CapEx for cabinets (USD 8,000–20,000) and batteries (USD 150–250 each) yields longer payback periods—challenging for small‑scale entrepreneurs.
Government subsidies (up to 30% CapEx support) help, but navigating grant processes can be bureaucratic.
Maintenance & Skilled Workforce
Mechanical and IoT components demand specialized technicians—currently scarce in Bangladesh’s nascent EV sector.
Training pipelines and certification programs must scale to meet 24/7 station servicing needs.
Regulatory Uncertainty
Lack of clear swap‑station licensing frameworks or safety codes delays approvals.
Frequent policy changes (e.g., EV import duties, tariff revisions) increase business risk for investors.
Competition with Fast Charging
Growing DC‑fast‑charging networks (50–150 kW) offer direct plug‑in alternatives—forcing swap operators to demonstrate superior cost/time advantages.
Hybrid models (“swap + charge”) may be required to capture diverse user segments.
Battery Lifecycle & Recycling
End‑of‑life battery management (collection, secondary‑use pipelines, recycling) is underdeveloped—raising environmental and regulatory concerns.
Partnerships with recycling firms and second‑life‑use integrators are essential for sustainable operations.
Data Security & Privacy
IoT connectivity and user apps collect sensitive rider and fleet data—necessitating robust cybersecurity measures and compliance with Bangladesh’s digital‑data policies.
Overcoming these challenges—through site‑sharing alliances, standardized battery protocols, targeted training programs, and regulatory engagement—will be pivotal for scaling battery swapping station in Bangladesh networks and realizing the country’s clean‑mobility ambitions.
Technical Expertise & R&D
Local Market Understanding: Choose vendors with proven deployments in similar emerging‑market contexts. SRE Power’s projects in Kenya and Indonesia demonstrate climate resilience and grid‑variability handling.
Innovation Roadmap: Partner with suppliers investing in IoT, predictive analytics, and next‑gen connectors. SRE Power’s 50+ R&D engineers continuously refine RFID, cloud software, and battery‑replacement robotics.
Product Portfolio & Modular Scalability
Slot Configurations: Ensure availability of 4, 8, 10, and 12‑slot cabinets to match pilot scale and future growth.
Expansion Kits: Opt for “plug‑and‑play” modules that stack additional compartments without major civil works, minimizing CapEx ramp‑up.
Manufacturing & Supply Chain
Local Assembly Options: Suppliers offering CKD/SKD kits reduce import duties. SRE’s factories in Dongguan, Malaysia, and Africa provide regional sources for faster lead times.
Quality Certifications: Insist on ISO 9001, CE, IP65, and OCPP compliance. Verify factory acceptance test (FAT) reports for all critical components.
Safety & Reliability
Multi‑Sensor Protection: Cabinetry must monitor over‑current, over‑voltage, temperature, and smoke—automatically isolating any anomaly.
Warranty & SLAs: Seek at least 12 months hardware warranty, plus guaranteed 24‑hour part replacements and local technical support agreements.
Software & Digital Ecosystem
Cloud Dashboard: Look for intuitive UIs displaying station status, battery health, transaction logs, and energy consumption.
API Integration: Ensure open RESTful or MQTT/OCPP interfaces for EV‑fleet management, ride‑hailing platforms, and payment gateways.
Local Service & After‑Sales
Regional Presence: Manufacturers with Bangladesh‑based service centers or certified partners guarantee rapid response.
SRE Power (Guangdong SRE Technology Ltd.)
• Global R&D since 2014; factories in China, Malaysia, Africa; CE & ISO certified; modular 4–24 slot Smart Swap Stations with IoT.
ION Energy
• Battery‑management expertise; BaaS partnerships; modular swap cabinets with advanced BMS integration.
Sun Mobility
• India‑based swap network; patented fast‑swap tech; local partner for rollouts in South Asia.
Lithium Urban Technologies
• Urban bus / cargo fleet focus; turnkey station + software for route optimization.
Exicom Tele‑Systems
• Telecom heritage; high‑reliability swap + DC charging hybrids; strong service network.
Ather Energy
• EV OEM with proprietary swap stations; seamless vehicle‑station integration for scooters.
Mahindra Electric
• Auto‑giant backing; swap solutions for light commercial vehicles and cargo trikes.
EVRE (Electric Vehicle Reverse Ecosystem)
• Startup innovator; lightweight 6‑slot cabinets; target Tier‑2 South Asian cities.
Orix Auto Infrastructure Services
• Asset‑finance group; capital‑backed swap + charge deployments with financing schemes.
Greenovation (Fictional Local JV)
• Hypothetical joint venture leveraging local Bangladesh manufacturing and international tech licensing—illustrates potential for local assembly and rapid scaling.
Each of these players offers distinct strengths—from SRE’s modular IoT‑native systems to Sun Mobility’s regional network experience. For battery swapping station in Bangladesh, operators should weigh local service footprints and BaaS models alongside pure‑play hardware capabilities.
Training Programs: Confirm availability of operator and technician workshops covering safety protocols, remote diagnostics, and preventive maintenance.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
CapEx vs. OpEx Analysis: Balance hardware costs against projected swap volumes, energy arbitrage (off‑peak charging), and subscription revenues.
Battery‑As‑A‑Service (BaaS): Evaluate leasing models to shift battery‑asset risk to the vendor, lowering initial investments by 20–40%.
Government Subsidies: Identify manufacturers experienced in navigating Bangladesh’s green energy incentives (e.g., reduced import tariffs, concessional loans).
Proven Case Studies & References
Regional Deployments: Request references from similar environments—monsoon‑prone, high‑humidity markets. SRE’s partnerships in Malaysia and Africa illustrate successful resilience and user‑adoption rates.
Customer Feedback: Interview existing operators about uptime statistics, maintenance responsiveness, and software reliability under heavy‑use scenarios.
Future‑Proofing & Co‑Innovation
Upgradability: Ensure hardware supports future firmware enhancements, 5G IoT modules, and compatibility with solid‑state battery chemistries.
R&D Collaboration: Large deployments may benefit from joint R&D—tailoring BMS algorithms to local grid‑voltage fluctuations or customizing cabinet designs for Dhaka’s traffic patterns.
By rigorously assessing these nine criteria—technical prowess, product breadth, manufacturing footprint, safety standards, software ecosystem, local support, TCO clarity, references, and upgrade pathways—you can select a battery swapping station manufacturer that not only delivers hardware but also a sustainable, scalable infrastructure tailored for battery swapping station in Bangladesh.
Interested in bangladesh swap station Contact us today to learn how our solutions can power your vehicles!
